Application
-
Power supply
-
Intelligence
-
Vehicle electronics
-
Medical care
-
Rail transit
-
Home appliances
-
Illumination

- Scan QR code
WeChat
Contact

- +86 18028688880
- +86 0755-28102519
- +86 0755-28102529
- winnertong@ysxdz.com
- No.201 of Longsheng Science Building in Longsheng industry district, Dalang, Longhua, Shenzhen, China
Solution to the power adapter
Source:Shenzhen Yushuoxin Electronic Co., LtdTime:2017-03-21
Semiconductor power adapter mainly includes two types, one is the internal AC / DC (AC / DC) power converter, built in the electronic products, may have multiple output voltage, such as desktop computer internal power supply; the other is the external single (AC / AC) power adapter, with a single output voltage, usually referred to as external power (EPS), widely used in printers, notebooks, LCD monitors and game consoles and other applications.
General power market trends for power adapters
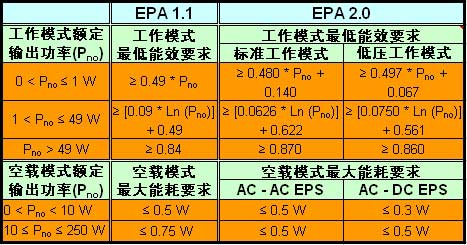
From the general market point of view, the power adapter mainly reflects some important trends. First, work efficiency and standby (no load) energy requirements are higher. For example, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Energy Star project was released in April 2008 for the 2.0 version of the external power supply specifications, from Table 1 comparison can be seen in the 2.0 version of the requirements of the specification than the 1.1 version of the specification. The EPA 2.0 specification for external power supplies will come into effect on November 1, 2008. In the desktop power supply and other internal power supply, "Energy Star" version 4.0 specification (EPA 4.0) the first phase of the requirements since July 20, 2007 to take effect. The specification requires a minimum of 80% energy efficiency for desktops under 20%, 50% and 100% load conditions. In addition, the updated Phase 1 specification requirements will take effect on July 1, 2009, will require the use of internal power of the computer under 50% load conditions, the lowest efficiency of up to 85%, while the 20% and 100% load Under the conditions of the minimum efficiency of 82%.
In addition to industry energy efficiency requirements such as Energy Star, some large OEM customers may have their own unique energy efficiency and energy requirements. For example, the EPA 4.0 specification for computer power supplies is mainly concerned with standby power consumption (≤1.0 W), dormancy power consumption (≤1.7 W), etc. for notebooks and tablets that use external power supplies. In contrast, The requirements for this type of power supply are mainly reflected in the energy efficiency under different load conditions, ie 0.7 W (input power Pin <1 W), 1.5 W (Pin <2 W), 10.7 W (Pin <12.6 W) and 17 W (75%, 85%, and 85%, respectively) under the load conditions of Pin <20 W. It is worth mentioning that the future of energy efficiency standards will continue to improve the requirements and evolution. For notebook AC-DC power adapter, for example, the industry in the no-load mode energy consumption of the higher level of about 300 mW or more, and the future no-load mode 150 mW energy consumption may become the target. Moreover, the requirements for multi-output adapters may also be incorporated into the standard.
Another important trend in the power adapter market is that customers need to have higher output power, smaller size adapters, which involve the use of new topology technologies. NCP1605 power factor correction (PFC) controller and NCP1396 resonant mode controller can be used to design 200W desktop adapter or 300W adapter. And from the notebook adapter, the power requirements have been from 50 W to 70 W range rose to more than 100 W level. In addition, such as Apple MacBook Air and Lenovo ThinkPad X300 and other new ultra-portable notebook power adapter is smaller and lighter. In addition to these trends, another noteworthy trend is the relaxation of power factor (PF) restrictions in the ENERGY STAR's official 2.0 specification for external power supplies. In fact, according to the IEC61000-3-2 harmonic current reduction standard that has been implemented in Europe and Japan, PFC is required for adapter applications with power greater than 75 W.
Currently on the market both the traditional "power factor correction + pulse width modulation" (PFC + PWM) two-stage architecture, there are two paragraphs into a single-stage PFC-based architecture. The two-stage architecture achieves a power factor of 0.9 at both 115 Vac and 230 Vac, and better performance in terms of dynamic response speed and ripple, but this architecture is a resource-intensive design that uses more Components such as control ICs, inductors, and MOSFETs, and may result in energy efficiency degradation in the operating mode. In contrast, another single-stage PFC architecture combines PWM and PFC segments to reduce control ICs , Inductance and MOSFET use, to achieve energy efficiency improvement and significant cost reduction. However, the external power supply of the single-stage PFC architecture has a power factor of only greater than 0.8 at 230 Vac, and there are many distances from the 0.9 limit. To achieve a power factor limit of 0.9, some modifications to the circuit are required , But this change will lose a few percentage points of energy efficiency.
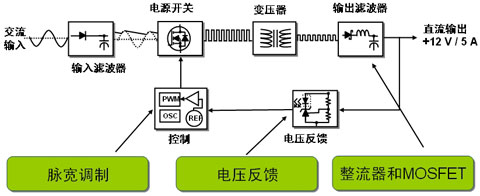
Therefore, in the ENERGY STAR official version 2.0 specification for external power supplies, the power factor requirements are limited to the external power supply with input power greater than 100 W and the test conditions for 115 Vac, while 230 Vac is not required; While external power supplies capable of operating at 115 Vac and 230 Vac are only required to meet the test requirements under 115 Vac in terms of power factor. In this way, with a higher cost, suitable for power adapter applications such as single-stage PFC will win a greater momentum of development. Challenges for Power Adapters Combining the general market trends of power adapters above, we can conclude that the main challenge for power adapters is to reduce no-load input power and improve overall energy efficiency; especially for notebook adapters, pay attention to standby, sleep And idle and other different modes of energy efficiency; improve power factor; below we will be in accordance with the application of different power levels, sharing Yu Shuo Xin semiconductor related solutions. Yixin Xin semiconductor power adapter solution 1) Input power less than 75 W adapter application As mentioned above, the input power is less than 75 W, the external power supply without PFC, the system is only the PWM section, the structure diagram shown in Figure 1. In this case, the flyback topology is usually used, the adapter can work at a fixed frequency (FF), but also work in the variable frequency (VF) of the controller (especially in quasi-resonant mode). In the rated load and light load conditions, to achieve higher energy efficiency at the same time, the key is to use the load conditions can be adjusted according to the working mode of intelligent controller.
Among them, the power range of 10 W to 50 W range of applications, you can use NCP1351 and NCP1216 and other devices. Among them, the NCP1351 uses a fixed turn-on time, variable off-time current mode control technology, will reduce the load when the low switching frequency, can provide excellent no-load energy consumption, and light load conditions to provide the best energy performance; When the frequency drops, the peak current gradually decreases to about 30% of the maximum peak current, can avoid the mechanical resonance of the transformer, thus greatly eliminating the audible noise, and maintain a good standby power performance. It is worth mentioning that, Yu Shuo Xin Semiconductor introduced the NCP1351 based GreenPointTM 40 W printer power adapter reference design. The reference design consumes less than 150 mW of standby power, while the currently used 40 W printer consumes about 450 mW in a similar situation. Under the rated load conditions, the design of the energy efficiency of up to 85%; and its use of the frequency of anti-technology, but also to its higher than 2 W light load conditions, energy efficiency higher than 80%. In addition to NCP1351 and NCP1216, Yu Shuo Xin Semiconductor will also introduce NCP1217 and NCP1380 and other new devices. And NCP1271, NCP1219 and NCP1288 and other fixed frequency controller (including NCP1219 and NCP1288 for new products, will soon be introduced), but also can be used NCP1377, NCP1337 and NCP1380 and other variable frequency Controller.
In addition to the PWM controller, power supply less than 75 W power adapter, you can also use a number of other Shixin Xin semiconductor devices. Such as the voltage feedback link, you can use TL431, TLV431, NCP100 and NCP4300 (for the second generation constant current constant voltage adapter) and other shunt regulator. In the case of rectifiers and MOSFETs, Yu Shuo Xin Semiconductor also offers a wide range of suitable devices, including all H series and L series Schottky diodes with voltages between 45 and 100 V and current between 3 and 10 A, and NCP4302 control Device. For example, the NCP4302 is an integrated synchronous rectifier (SR) controller and driver that integrates all the control and protection functions required for synchronous rectification in flyback converters, supporting any type of flyback topology (Continuous conduction mode, quasi-resonant mode or discontinuous conduction mode), is ideal for adapters, chargers and set-top boxes and other space-sensitive applications. 2) Input power greater than 75 W In contrast, according to the IEC61000-3-2 standard, if the input power is greater than 75 W, you need to increase the PFC, which constitutes the PFC + PWM two-stage external power supply architecture, as shown in Figure 3. In this power class PFC segment, critical conduction mode (CRM) is widely used; in the main converter section, there are flyback, forward active clamp and resonant LLC and other topologies to choose from The
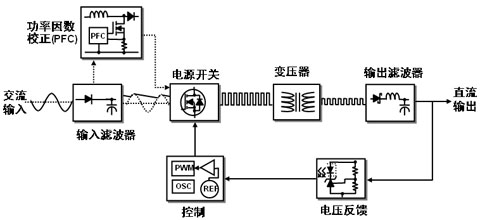

Table 1: "Energy Star" external power specification comparison (Ln is the natural logarithm of rated output power)
General power market trends for power adapters
From the general market point of view, the power adapter mainly reflects some important trends. First, work efficiency and standby (no load) energy requirements are higher. For example, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Energy Star project was released in April 2008 for the 2.0 version of the external power supply specifications, from Table 1 comparison can be seen in the 2.0 version of the requirements of the specification than the 1.1 version of the specification. The EPA 2.0 specification for external power supplies will come into effect on November 1, 2008. In the desktop power supply and other internal power supply, "Energy Star" version 4.0 specification (EPA 4.0) the first phase of the requirements since July 20, 2007 to take effect. The specification requires a minimum of 80% energy efficiency for desktops under 20%, 50% and 100% load conditions. In addition, the updated Phase 1 specification requirements will take effect on July 1, 2009, will require the use of internal power of the computer under 50% load conditions, the lowest efficiency of up to 85%, while the 20% and 100% load Under the conditions of the minimum efficiency of 82%.
In addition to industry energy efficiency requirements such as Energy Star, some large OEM customers may have their own unique energy efficiency and energy requirements. For example, the EPA 4.0 specification for computer power supplies is mainly concerned with standby power consumption (≤1.0 W), dormancy power consumption (≤1.7 W), etc. for notebooks and tablets that use external power supplies. In contrast, The requirements for this type of power supply are mainly reflected in the energy efficiency under different load conditions, ie 0.7 W (input power Pin <1 W), 1.5 W (Pin <2 W), 10.7 W (Pin <12.6 W) and 17 W (75%, 85%, and 85%, respectively) under the load conditions of Pin <20 W. It is worth mentioning that the future of energy efficiency standards will continue to improve the requirements and evolution. For notebook AC-DC power adapter, for example, the industry in the no-load mode energy consumption of the higher level of about 300 mW or more, and the future no-load mode 150 mW energy consumption may become the target. Moreover, the requirements for multi-output adapters may also be incorporated into the standard.
Another important trend in the power adapter market is that customers need to have higher output power, smaller size adapters, which involve the use of new topology technologies. NCP1605 power factor correction (PFC) controller and NCP1396 resonant mode controller can be used to design 200W desktop adapter or 300W adapter. And from the notebook adapter, the power requirements have been from 50 W to 70 W range rose to more than 100 W level. In addition, such as Apple MacBook Air and Lenovo ThinkPad X300 and other new ultra-portable notebook power adapter is smaller and lighter. In addition to these trends, another noteworthy trend is the relaxation of power factor (PF) restrictions in the ENERGY STAR's official 2.0 specification for external power supplies. In fact, according to the IEC61000-3-2 harmonic current reduction standard that has been implemented in Europe and Japan, PFC is required for adapter applications with power greater than 75 W.
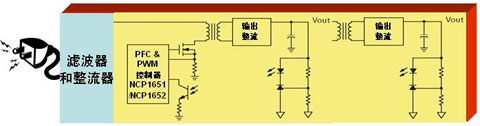
Currently on the market both the traditional "power factor correction + pulse width modulation" (PFC + PWM) two-stage architecture, there are two paragraphs into a single-stage PFC-based architecture. The two-stage architecture achieves a power factor of 0.9 at both 115 Vac and 230 Vac, and better performance in terms of dynamic response speed and ripple, but this architecture is a resource-intensive design that uses more Components such as control ICs, inductors, and MOSFETs, and may result in energy efficiency degradation in the operating mode. In contrast, another single-stage PFC architecture combines PWM and PFC segments to reduce control ICs , Inductance and MOSFET use, to achieve energy efficiency improvement and significant cost reduction. However, the external power supply of the single-stage PFC architecture has a power factor of only greater than 0.8 at 230 Vac, and there are many distances from the 0.9 limit. To achieve a power factor limit of 0.9, some modifications to the circuit are required , But this change will lose a few percentage points of energy efficiency.

Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the adapter structure for a single-stage PFC architecture
Therefore, in the ENERGY STAR official version 2.0 specification for external power supplies, the power factor requirements are limited to the external power supply with input power greater than 100 W and the test conditions for 115 Vac, while 230 Vac is not required; While external power supplies capable of operating at 115 Vac and 230 Vac are only required to meet the test requirements under 115 Vac in terms of power factor. In this way, with a higher cost, suitable for power adapter applications such as single-stage PFC will win a greater momentum of development. Challenges for Power Adapters Combining the general market trends of power adapters above, we can conclude that the main challenge for power adapters is to reduce no-load input power and improve overall energy efficiency; especially for notebook adapters, pay attention to standby, sleep And idle and other different modes of energy efficiency; improve power factor; below we will be in accordance with the application of different power levels, sharing Yu Shuo Xin semiconductor related solutions. Yixin Xin semiconductor power adapter solution 1) Input power less than 75 W adapter application As mentioned above, the input power is less than 75 W, the external power supply without PFC, the system is only the PWM section, the structure diagram shown in Figure 1. In this case, the flyback topology is usually used, the adapter can work at a fixed frequency (FF), but also work in the variable frequency (VF) of the controller (especially in quasi-resonant mode). In the rated load and light load conditions, to achieve higher energy efficiency at the same time, the key is to use the load conditions can be adjusted according to the working mode of intelligent controller.

Figure 2: Power adapter architecture with power less than 75 W
Among them, the power range of 10 W to 50 W range of applications, you can use NCP1351 and NCP1216 and other devices. Among them, the NCP1351 uses a fixed turn-on time, variable off-time current mode control technology, will reduce the load when the low switching frequency, can provide excellent no-load energy consumption, and light load conditions to provide the best energy performance; When the frequency drops, the peak current gradually decreases to about 30% of the maximum peak current, can avoid the mechanical resonance of the transformer, thus greatly eliminating the audible noise, and maintain a good standby power performance. It is worth mentioning that, Yu Shuo Xin Semiconductor introduced the NCP1351 based GreenPointTM 40 W printer power adapter reference design. The reference design consumes less than 150 mW of standby power, while the currently used 40 W printer consumes about 450 mW in a similar situation. Under the rated load conditions, the design of the energy efficiency of up to 85%; and its use of the frequency of anti-technology, but also to its higher than 2 W light load conditions, energy efficiency higher than 80%. In addition to NCP1351 and NCP1216, Yu Shuo Xin Semiconductor will also introduce NCP1217 and NCP1380 and other new devices. And NCP1271, NCP1219 and NCP1288 and other fixed frequency controller (including NCP1219 and NCP1288 for new products, will soon be introduced), but also can be used NCP1377, NCP1337 and NCP1380 and other variable frequency Controller.
In addition to the PWM controller, power supply less than 75 W power adapter, you can also use a number of other Shixin Xin semiconductor devices. Such as the voltage feedback link, you can use TL431, TLV431, NCP100 and NCP4300 (for the second generation constant current constant voltage adapter) and other shunt regulator. In the case of rectifiers and MOSFETs, Yu Shuo Xin Semiconductor also offers a wide range of suitable devices, including all H series and L series Schottky diodes with voltages between 45 and 100 V and current between 3 and 10 A, and NCP4302 control Device. For example, the NCP4302 is an integrated synchronous rectifier (SR) controller and driver that integrates all the control and protection functions required for synchronous rectification in flyback converters, supporting any type of flyback topology (Continuous conduction mode, quasi-resonant mode or discontinuous conduction mode), is ideal for adapters, chargers and set-top boxes and other space-sensitive applications. 2) Input power greater than 75 W In contrast, according to the IEC61000-3-2 standard, if the input power is greater than 75 W, you need to increase the PFC, which constitutes the PFC + PWM two-stage external power supply architecture, as shown in Figure 3. In this power class PFC segment, critical conduction mode (CRM) is widely used; in the main converter section, there are flyback, forward active clamp and resonant LLC and other topologies to choose from The

Figure 3: PFC + PWM two-stage external power supply architecture with input power greater than 75 W.
If we further refine this power range greater than 75 W, we can divide it into 75 to 120 W and 120 to 250 W applications.
Next article:None
Previous article:None
Recommend
- 2017-03-21Solution to the power adapter
